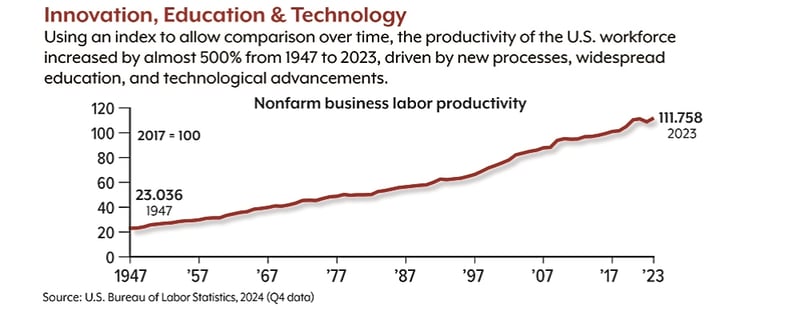
Productivity of U.S. workers increased by 2.7% in 2023 — well above the average annual rate of 2.1% since
the end of World War II, and a dramatic change from 2022, when productivity dropped by 2.0%. It's also a
big improvement over the 0.9% growth rate in 2021.1
According to the nonpartisan Congressional Research Service, "Productivity growth is a primary driver of
long-term economic growth and improvements in living standards."2 On a more immediate level, the
productivity surge in 2023 may help explain why the U.S. economy was able to grow at a strong pace while
inflation dropped.
Doing more with less
Broadly, productivity is the ratio of output to inputs. A productivity increase means that output increases
faster than inputs, essentially producing more with less.
The most commonly cited productivity measure for the U.S. economy is labor productivity for the nonfarm
business sector (the data cited in the first paragraph of this report). In simple terms, this is the value of
goods and services produced per hour of labor. The nonfarm business sector comprises most U.S.
business activity excluding farms, general government, and nonprofits.
Boosting GDP while fighting inflation
The 2.7% increase in 2023 means that, on average, 2.7% more value was created for each hour of labor.
This helps boost gross domestic product (GDP), while also helping to control inflation by holding back the
wage-price spiral, which can push inflation out of control.
In a tight employment market, as we have had for some time, a shortage of workers can force businesses
to offer higher wages, which they pass on to consumers as higher prices. Because consumers are then
earning more at their jobs, they demand more goods and services and are willing to pay higher prices,
which pushes businesses to hire more workers at higher wages, continuing the cycle. Increased
productivity allows business to keep prices lower even as they pay workers more. This seems to have
occurred in 2023, with average hourly wages rising by 4.3%, while inflation dropped to 3.4% — the first time
since the pandemic that wages increased faster than inflation.3
Compensating for demographics
Increasing productivity is especially important for the U.S. economy because of lower birth rates, the aging
of the population, and more young people staying in school. The labor force participation rate, which
measures the percentage of people age 16 and older who are working or looking for work, peaked in early
2000 and has trended downward since then.4 Higher productivity enables a smaller workforce to drive
economic growth on a level that would require a larger workforce without productivity gains.
Why is productivity increasing and can it be sustained?
Increases in labor productivity are typically driven by improved tools and technology, more efficient
processes and organizations, and increased worker experience, education, and training. The proliferation
of computers in the workplace spurred a productivity surge in the 1990s, and some analysts point to
artificial intelligence (AI) as contributing to the 2023 increase. It's possible that AI has already improved
some businesses, but any large-scale impact may take years, as businesses integrate AI through worker
training and new processes. As this unfolds, AI could help drive a long-term productivity surge.
A more immediate explanation for the current increase may be adjustment and experience with the hybrid
work model. A recent survey found that 43% of remote workers felt working from home makes them more
productive, while only 14% believed it makes them less productive. (Another 43% said it makes no
difference.)5 The ideal situation would allow employees to work in the most productive environment. Three
years after the pandemic, businesses may be improving that balance, and it's possible that further
developments in hybrid work could continue to drive productivity gains for some time.
New businesses can spur productivity through innovation, filling specialized niches, and producing specific
goods or services more efficiently. New business applications surged during and after the pandemic, with
more than 20 million from 2020 to 2023. Only about 10% of applications turn into businesses, but some
new enterprises may already be making a difference, and the surge of entrepreneurship bodes well for
future productivity.6
A less positive factor may be that some companies laid off employees and made other changes in 2023 in
anticipation of a recession that never materialized. Layoffs typically target the least productive employees,
and remaining employees may increase their productivity to maintain production levels. While this "lean"
model is not always sustainable, it can boost productivity in the short term, and technology and more
efficient processes may enable some businesses to stay lean.
Volatile data
Measuring productivity is difficult, especially in service industries, which now comprise the largest sector of
U.S. economic activity. For this reason, productivity data can be volatile and often changes with revision.
(The 2.7% Q4 data is preliminary.) Even so, the surge in 2023 seems solid, and enhancements such as
artificial intelligence, hybrid work, and new business innovation could usher in a sustained period of
productivity growth. The Bureau of Labor Statistics releases productivity data quarterly, with Q1 2024 data
coming in May. You might keep an eye out for a continuing trend.
1, 3–4) U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2024
2) Congressional Research Service, January 3, 2023
5) Bloomberg, January 30, 2024
6) U.S. Chamber of Commerce, February 2, 2024

